Howe Roof Truss Method Of Sections

Truss analysis method of sections.
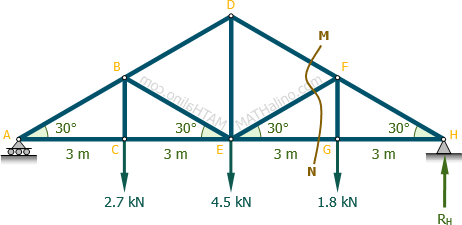
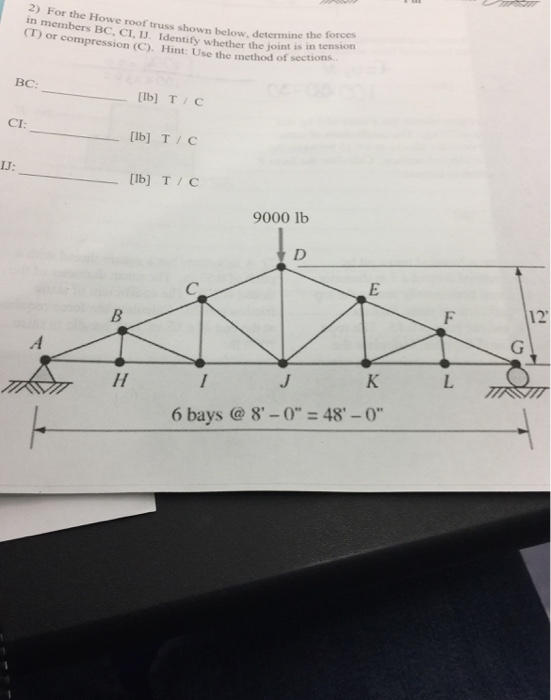
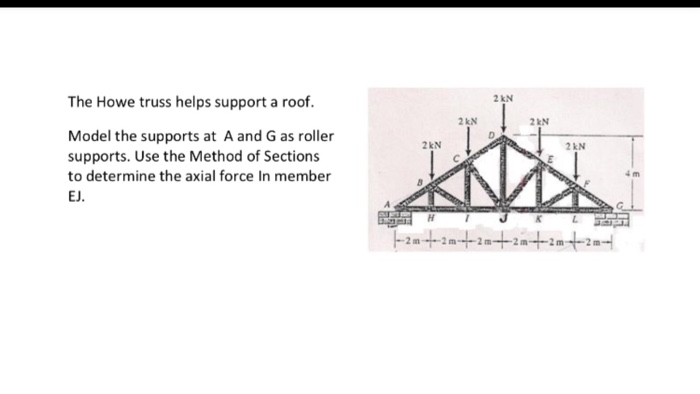
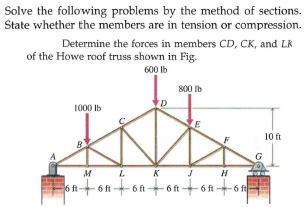
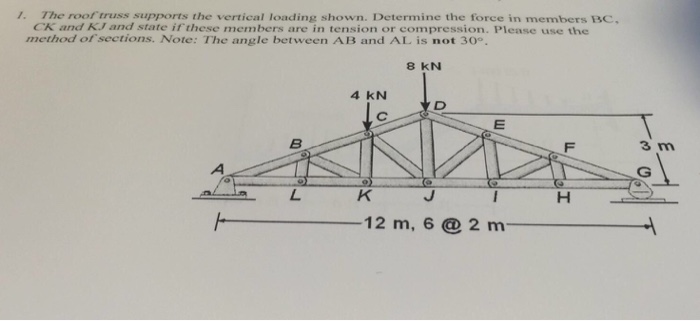
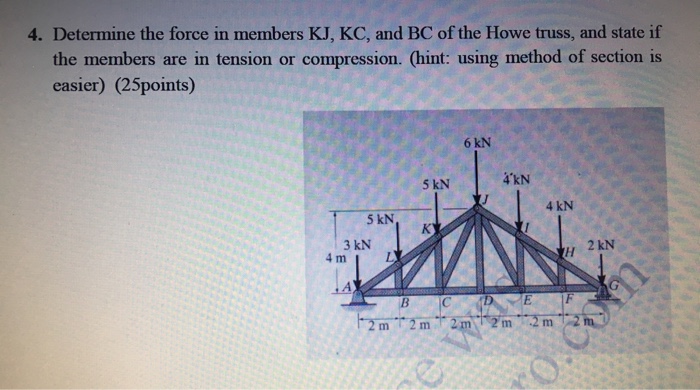
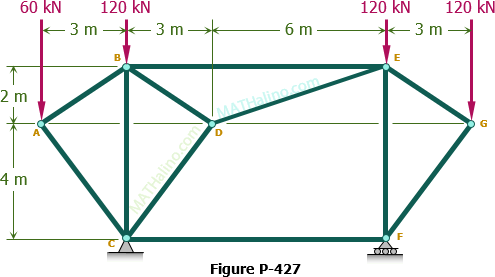
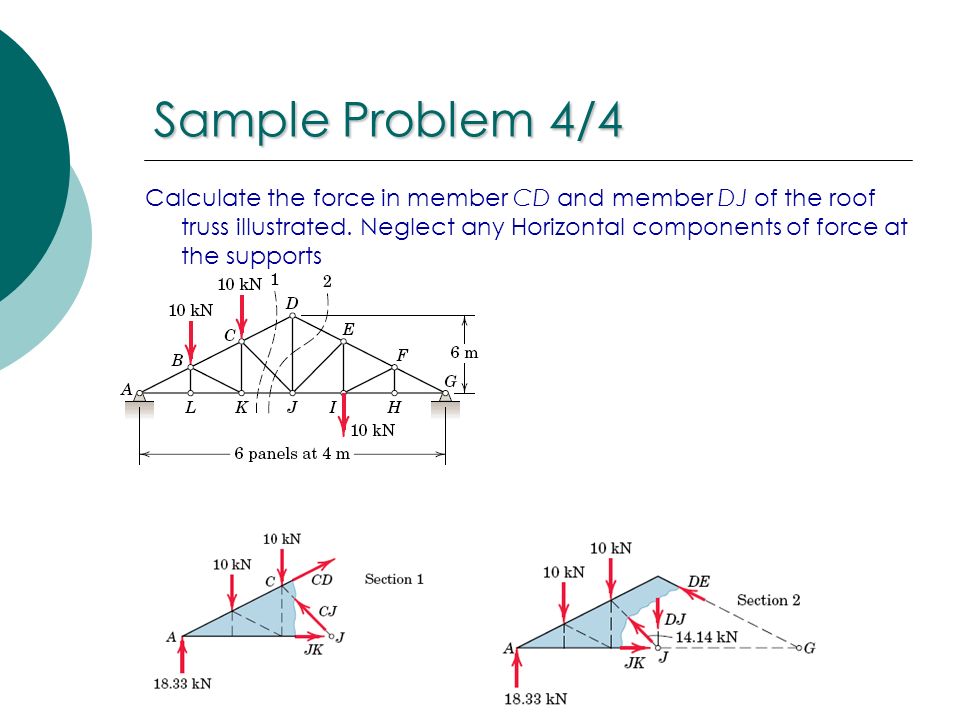
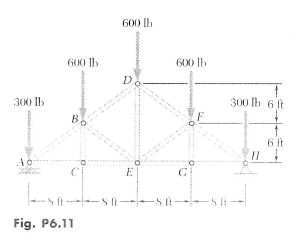
Howe roof truss method of sections. In this method we will cut the truss into two sections by passing a cutting plane through the members whose internal forces we wish to determine. I calculate support reactions ii cut and isolate iii apply. Example problem using method of sections for truss analysis statics and structural analysis. For the howe roof truss shown determine the forces in members bc ci and ij.
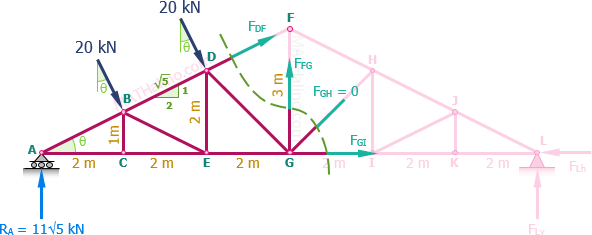
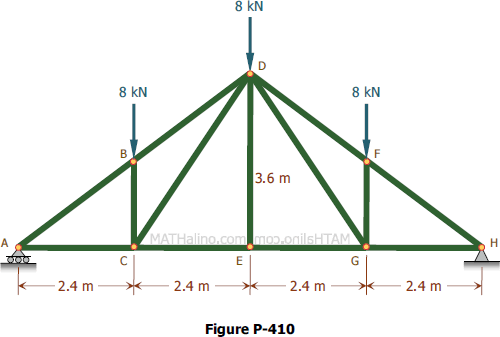
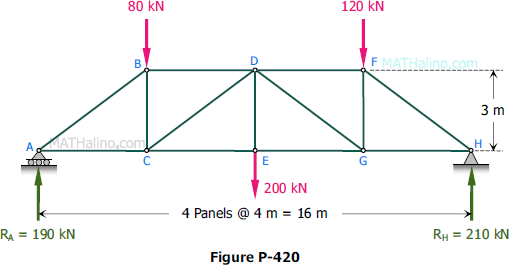
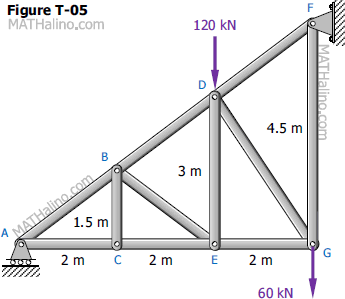
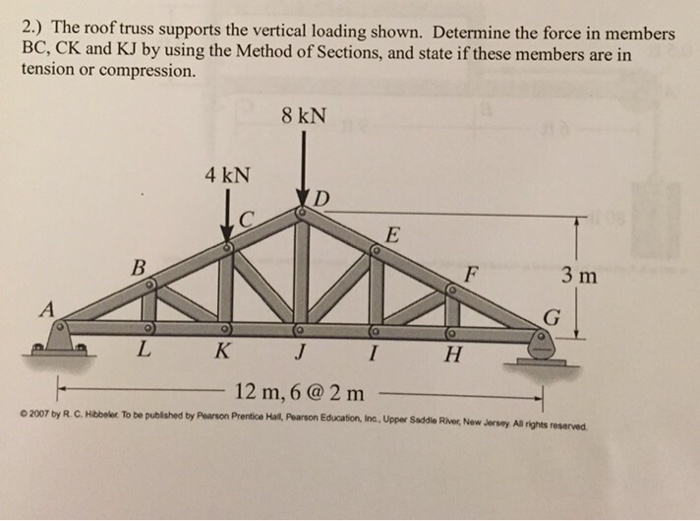
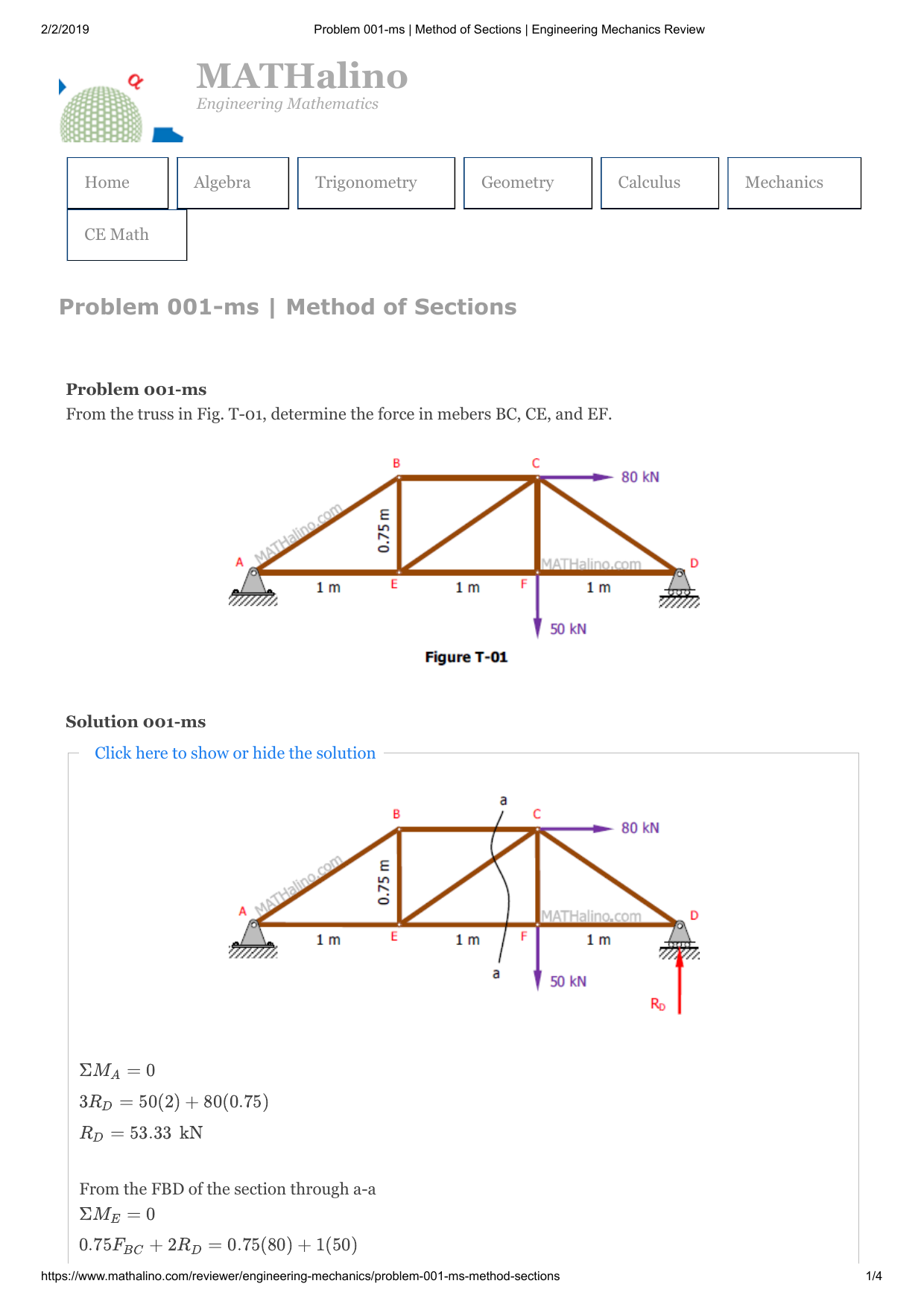
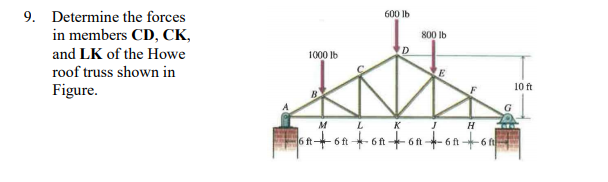
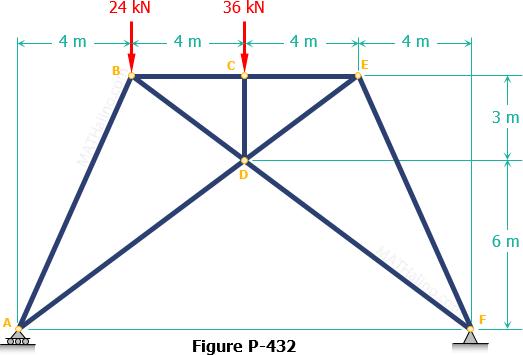
90 20 ratings for this solution. The method of sections enables one to determine forces in specific truss members directly. Problem 423 howe roof truss by method of sections problem 423 use the method of sections to determine the force acting in members df ef and eg of the howe truss described in problem 409. For problem use the method of section.
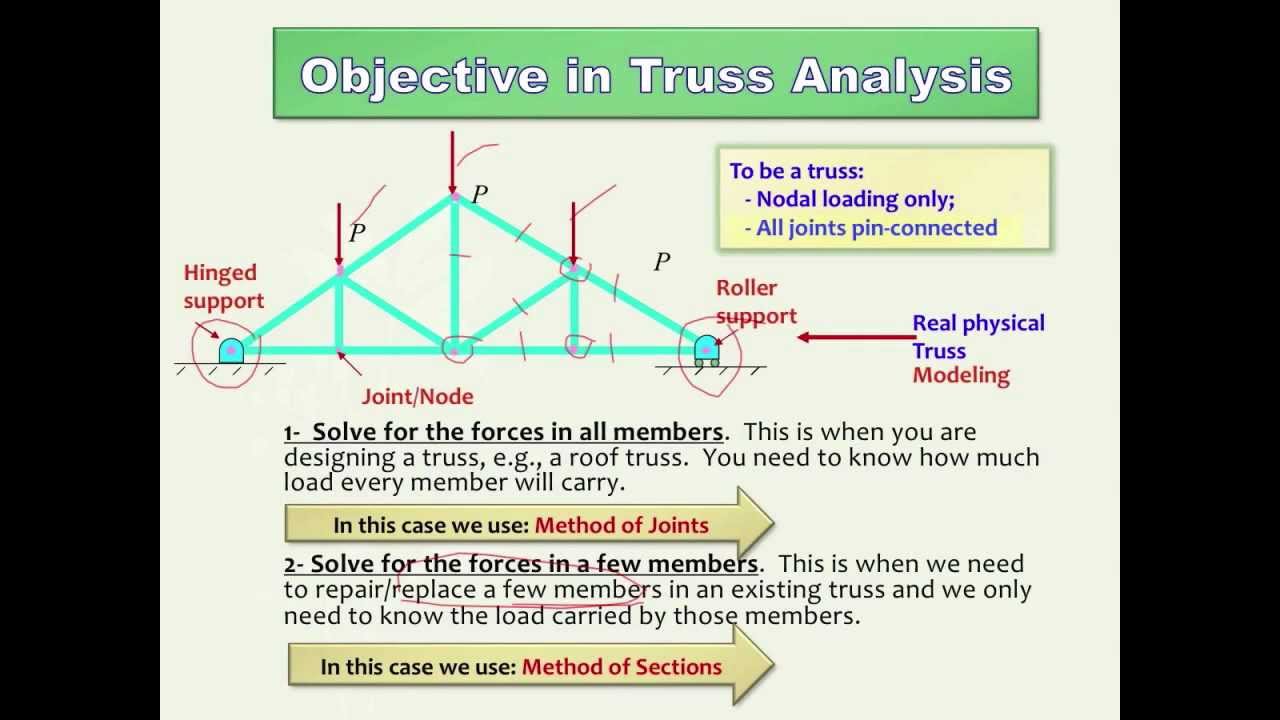
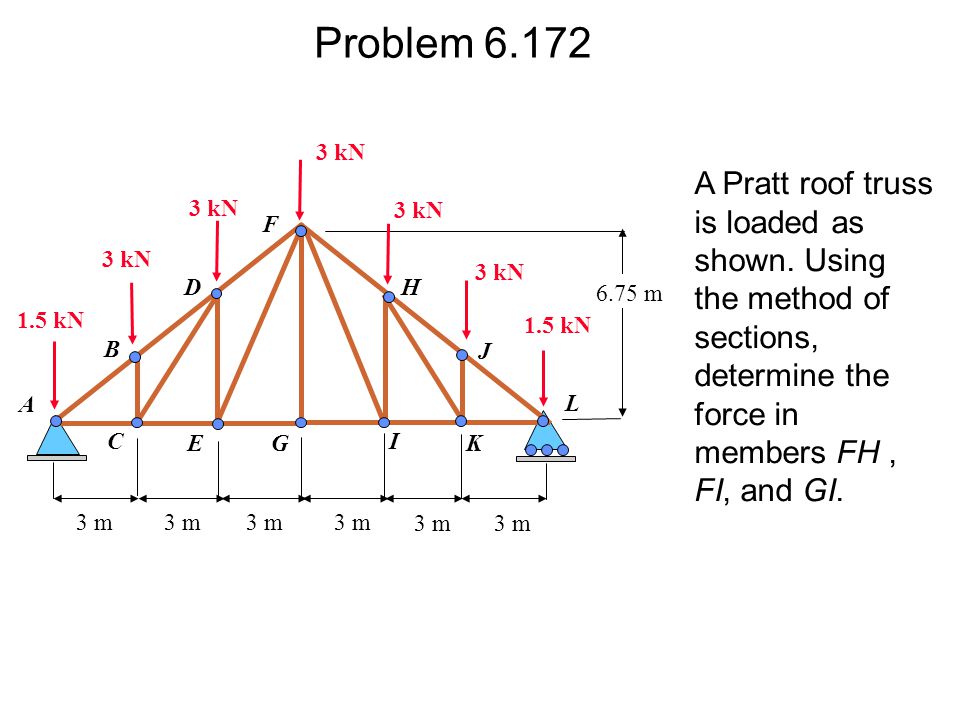
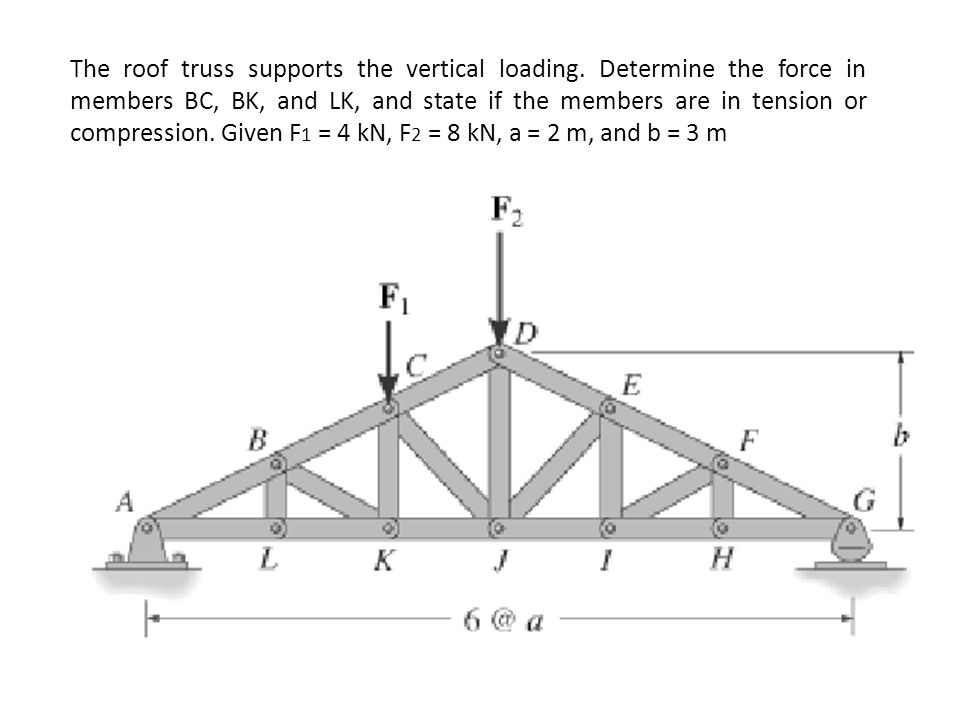
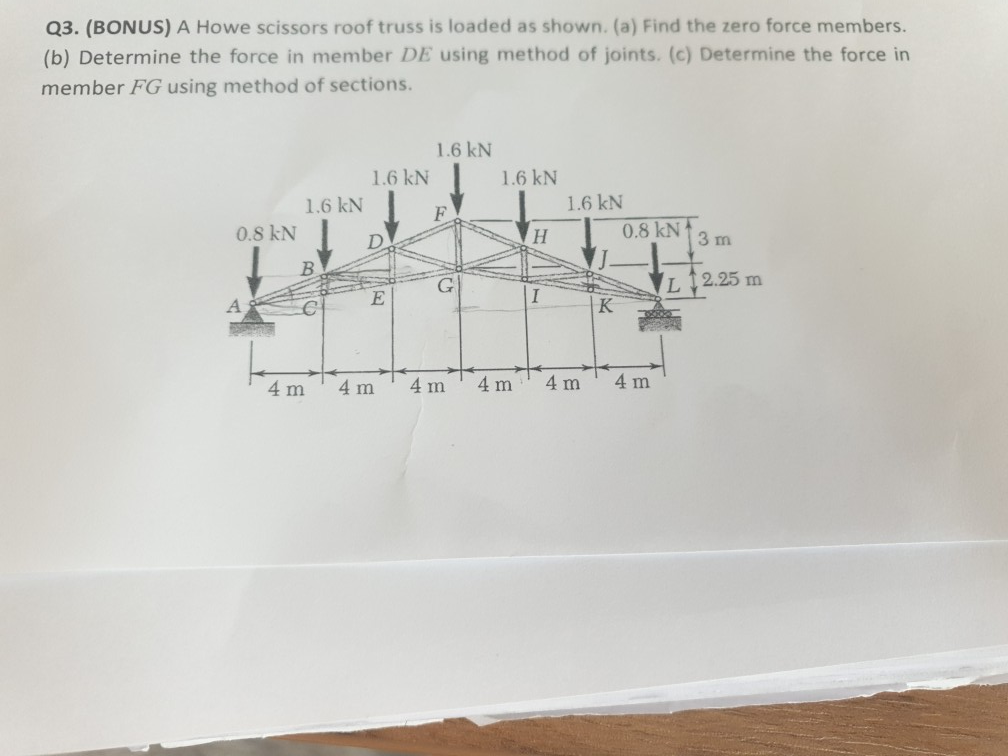
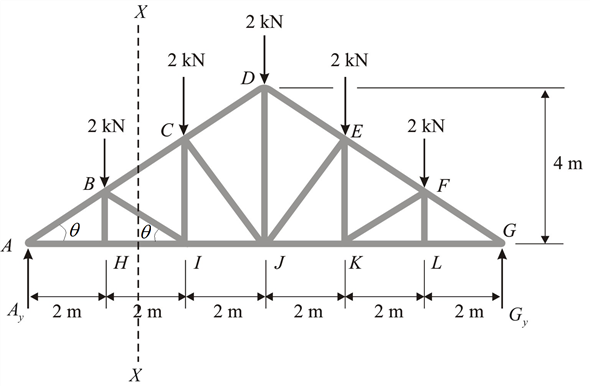
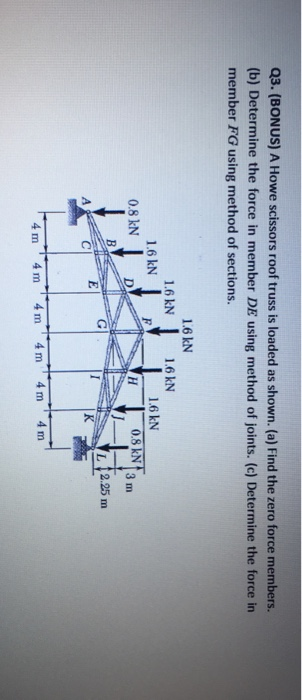
Structural mechanics pratt truss worked example. Having demonstrated to you the method of joints we now move on to see the method of sections that directly gives the force on a desired member of the truss. 14 determine the force in each of the members located to the left of fg for the scissors roof truss shown. State whether each member is in.
This free online truss and roof calculator generates the axial forces and reactions of completely customisable 2d truss structures. State whether each member is in tension or compression. This rafter truss calculator has a range of applications including being used as a wood truss calculator roof truss calculator roof rafter calculator scissor truss calculator or for roof framing. It involves taking a cut through a number of members to evaluate their axial forces and use this as our basis to solve the rest of the truss structure.
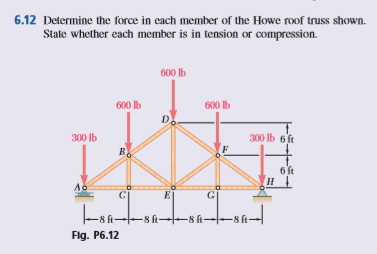
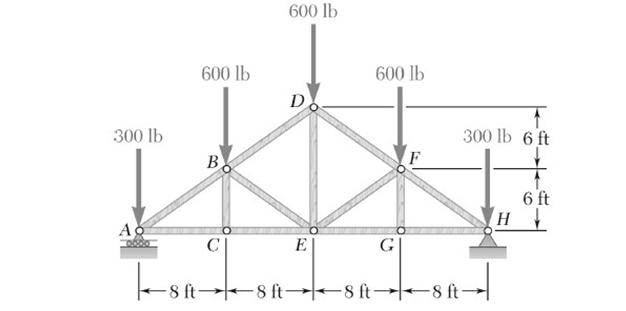
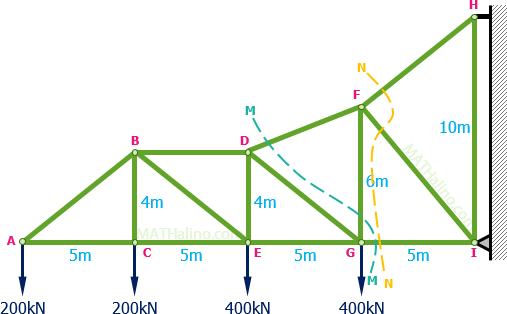
10 determine the force in each member of the howe roof truss shown. As the name suggests in method of sections we make sections through a truss and then calculate the force in the members of the truss though which the. Method of sections involves cutting the truss into two portions free body diagrams fbd by passing an imaginary section through the members whose forces are desired. Desired member forces are determined by considering equilibrium of one of the two.